How To Create A Dataframe With Different Number Of Rows
Different ways to create Pandas Dataframe
Pandas DataFrame is a 2-dimensional labeled data structure with columns of potentially different types. It is generally the most commonly used pandas object.
Pandas DataFrame can be created in multiple ways. Let's discuss different ways to create a DataFrame one by one.
Method #1: Creating Pandas DataFrame from lists of lists.
Attention geek! Strengthen your foundations with the Python Programming Foundation Course and learn the basics.
To begin with, your interview preparations Enhance your Data Structures concepts with the Python DS Course. And to begin with your Machine Learning Journey, join the Machine Learning - Basic Level Course
Python3
import pandas as pd
data = [[ 'tom' , 10 ], [ 'nick' , 15 ], [ 'juli' , 14 ]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns = [ 'Name' , 'Age' ])
df
Output:

Method #2: Creating DataFrame from dict of narray/lists
To create DataFrame from dict of narray/list, all the narray must be of same length. If index is passed then the length index should be equal to the length of arrays. If no index is passed, then by default, index will be range(n) where n is the array length.
Python3
import pandas as pd
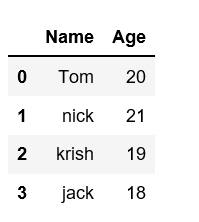
data = { 'Name' :[ 'Tom' , 'nick' , 'krish' , 'jack' ],
'Age' :[ 20 , 21 , 19 , 18 ]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df
Output:
Method #3: Creates a indexes DataFrame using arrays.
Python3
import pandas as pd
data = { 'Name' :[ 'Tom' , 'Jack' , 'nick' , 'juli' ],
'marks' :[ 99 , 98 , 95 , 90 ]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = [ 'rank1' ,
'rank2' ,
'rank3' ,
'rank4' ])
df
Output:

Method #4: Creating Dataframe from list of dicts
Pandas DataFrame can be created by passing lists of dictionaries as a input data. By default dictionary keys taken as columns.
Python3
import pandas as pd
data = [{ 'a' : 1 , 'b' : 2 , 'c' : 3 },
{ 'a' : 10 , 'b' : 20 , 'c' : 30 }]
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df
Output:

Another example to create pandas DataFrame by passing lists of dictionaries and row indexes.
Python3
import pandas as pd
data = [{ 'b' : 2 , 'c' : 3 }, { 'a' : 10 , 'b' : 20 , 'c' : 30 }]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = [ 'first' , 'second' ])
df
Output:

Another example to create pandas DataFrame from lists of dictionaries with both row index as well as column index.
Python3
import pandas as pd
data = [{ 'a' : 1 , 'b' : 2 },
{ 'a' : 5 , 'b' : 10 , 'c' : 20 }]
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data, index = [ 'first' ,
'second' ],
columns = [ 'a' , 'b' ])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data, index = [ 'first' ,
'second' ],
columns = [ 'a' , 'b1' ])
print (df1, "\n" )
print (df2)
Output:

Method #5: Creating DataFrame using zip() function.
Two lists can be merged by using list(zip()) function. Now, create the pandas DataFrame by calling pd.DataFrame() function.
Python3
import pandas as pd
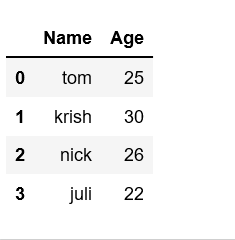
Name = [ 'tom' , 'krish' , 'nick' , 'juli' ]
Age = [ 25 , 30 , 26 , 22 ]
list_of_tuples = list ( zip (Name, Age))
list_of_tuples
df = pd.DataFrame(list_of_tuples,
columns = [ 'Name' , 'Age' ])
df
Output:
Method #6: Creating DataFrame from Dicts of series.
To create DataFrame from Dicts of series, dictionary can be passed to form a DataFrame. The resultant index is the union of all the series of passed indexed.
Python3
import pandas as pd
d = { 'one' : pd.Series([ 10 , 20 , 30 , 40 ],
index = [ 'a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' ]),
'two' : pd.Series([ 10 , 20 , 30 , 40 ],
index = [ 'a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' ])}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
df
Output:

How To Create A Dataframe With Different Number Of Rows
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/different-ways-to-create-pandas-dataframe/
Posted by: boothbyfirad1964.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create A Dataframe With Different Number Of Rows"
Post a Comment